| Collection Home Page -> | List of Species and Strains of IEGM
Collection -> |
Rhodococcus ruber |

Rhodococcus ruber (Kruse 1896) Goodfellow and Alderson 1977
IEGM 231
Coidentity: VKPM AC-1899
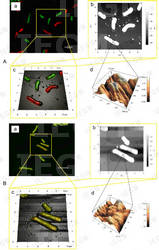
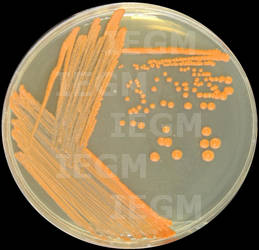
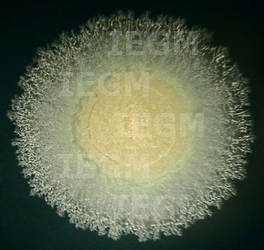
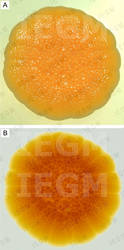
<- 1988, I.B. Ivshina, OEGM 29-1B-1. Isolated from: water, spring, Olkhovski oil-extracting enterprise, Perm region, Russia. Taxonomy/description: shows positive result with Rhodococcus ruber primers in species-specific PCR (245); 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis (GenBank accession number KF155234); whole genome was sequenced and deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank under accession numbers CCSD01000001 to CCSD01000115 (343); (55, 95, 97). Properties: uses n-dodecane, n-hexadecane, propane and n-butane as a sole carbon source (28, 95, 327, 424, 444); produces biosurfactants when growing on n-alkanes (C12-C17) (74, 248, 254, 327, 347, 348, 428); degrades high-porous ceramic materials (237); degrades paracetamol (265) and sodium diclofenac (29, 410, 425); forms cholesterol oxidase; resistant to Mo6+ (5.0 mM), VO2+ (25.0 mM), VO43- (100.0 mM), VO3- (>250.0 mM), accumulates molybdenum and nickel (286, 329, 423); adheres to liquid hydrocarbons (317, 320, 422); bioremediation agent for oil-contaminated soil (28, 324); resistant to 1-butanol, ethanol (341, 349); produces glycolipid biosurfactant with immunomodulating properties (344, 415). The dependence of the decrease in phytotoxicity of molybdenum after treatment Rhodococcus-biosurfactants seeds was revealed (36). (Medium 2, 5, 8 or 11, 28oC).
Reference(s): 28, 29, 36, 55, 74, 95, 97, 237, 245, 248, 252, 253, 254, 257, 258, 261, 263, 264, 265, 267, 268, 269, 271, 275, 277, 286, 294, 314, 317, 320, 324, 327, 329, 341, 343, 344, 347, 348, 349, 407, 410, 414, 415, 417, 418, 422, 423, 424, 425, 426, 428, 434, 444